ABC Heart Fail Cardiomyop 2025; 5(1): e20240053
Dilated Cardiomyopathy Associated With A Novel Truncated Filamin C Variant Mimicking Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Diagnostic Challenge
Introduction
Filamins interconnect actin filaments and form a broad network in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells by anchoring membrane proteins to the cytoskeleton. Filamin C, encoded by the FLNC gene, is one of three filamin-related proteins and binds to several proteins in the Z-disc of the sarcomere. Mutations in FLNC were initially associated with skeletal myofibrillar myopathy but are now recognized as associated with dilated and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy phenotypes, with autosomal dominant inheritance and an estimated penetrance of 92–97%, and are included in the genetic screening of patients with arrhythmogenic heart disease and sudden cardiac death. The prevalence of pathogenic FLNC variants is 1–4.5% among patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and up to 6% in patients with arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy.,
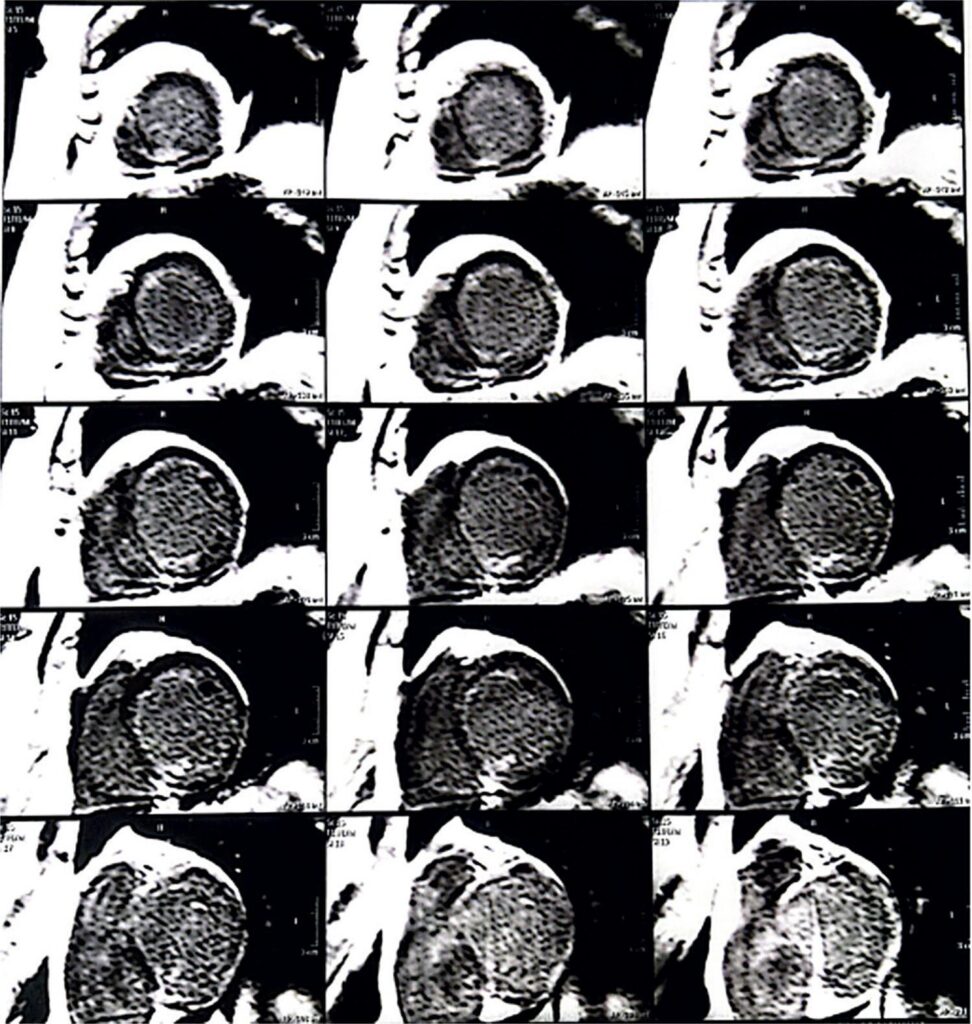
We describe the case of a patient with a novel truncated variant in the filamin C gene with a DCM phenotype who, during clinical follow-up and etiological investigation, presented imaging exams mimicking cardiac amyloidosis.
[…]
363