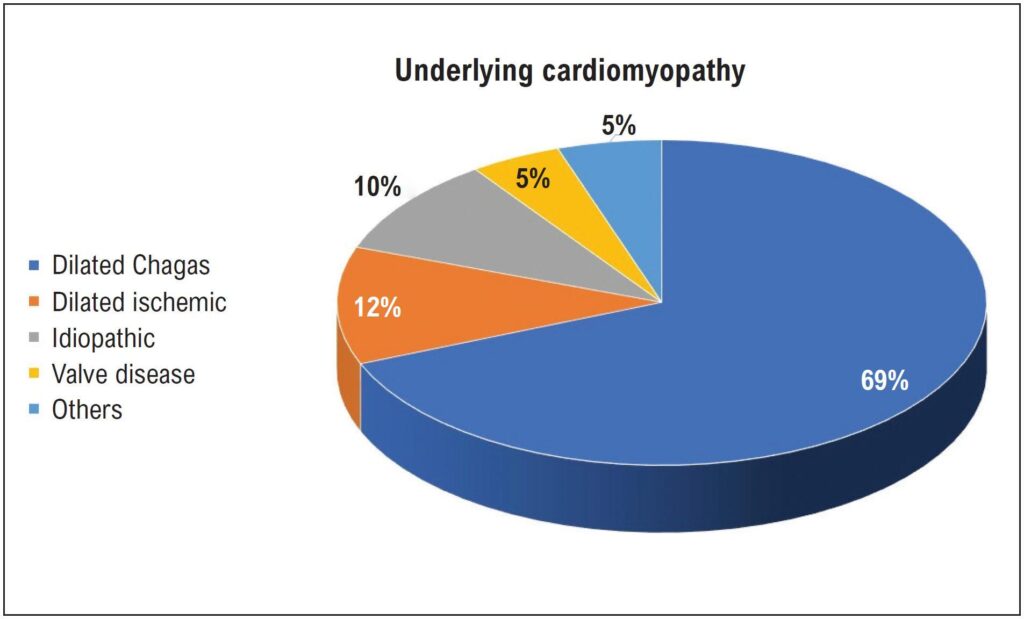
ABC Heart Fail Cardiomyop 2022; 2(2): 146-151
Cost-Effectiveness of Heart Transplantation: Data from a Referral Center in the Central-West Region of Brazil
Abstract
Background:
In Brazil, heart transplantation is fully funded by the Brazilian Unified Health System.
Objectives:
The objective of this study is to explore, for the first time, the cost-effectiveness profile of heart transplantation in a convenience sample, in a referral center in the Central-West Region of Brazil.
Methods:
Costs related to transplant hospitalization were evaluated, including those related to the surgical procedure, as well as hospitalization in the intensive care unit and in the inpatient ward, until patients were discharged. Costs associated with professional remuneration, fees, materials, and medications were computed. In order to assess effectiveness, post-transplant survival was used. For survivors, survival time was censored until the last contact recorded in the medical records of the transplant clinic. The cost-effectiveness ratio was expressed in Brazilian reals (BRL) per year of life saved.
Results:
We observed that the cost-effectiveness ratio was 25,806 BRL/year of life saved. Considering the average survival projected by Kaplan-Meier analysis, the cost-effectiveness ratio was 6,842 BRL/year of life saved.
Conclusion:
This result demonstrates a good cost-effectiveness ratio when compared to international studies that have evaluated this parameter. We did not, however, assess the micro-costing of the program and its feasibility for the institution. Given that this is a single-center study, the evaluation of other transplant centers is necessary in order to better elucidate this scenario.
875