ABC Heart Fail Cardiomyop 2021; 1(2): 95-97
How to Treat Heart Failure in Patients with Cardiac Amyloidosis
Abstract
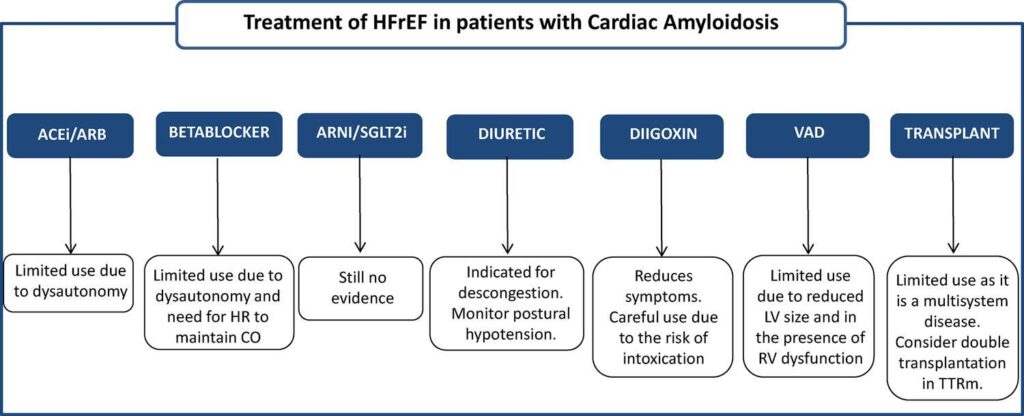
Amyloidosis is a multisystem disease characterized by deposition of fibrillar proteins in different tissues, the heart being one of the sites of amyloid deposition. Cardiac amyloidosis may present as a restrictive syndrome with symptoms of heart failure (HF). Treatment includes prognosis-modifying medications in HF; their optimization, however, is a challenge due to the frequent adverse effects in this population. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade should be carried out using low doses because, due to autonomic dysfunction, these drugs may cause hypotension and fatigue. The use of diuretics is necessary to maintain euvolemic status and optimized preload; however, due to the ventricular restriction present in cardiac amyloidosis, these medications should be used with caution. In patients with amyloidosis who progress to advanced HF, there are particularities in relation to indications for heart transplantation or long-term ventricular assist devices. The objective of this article is to review the treatment alternatives for HF in patients with cardiac amyloidosis.
Amyloidosis is a multisystem disease characterized by the deposition of fibrillar proteins with specific structural characteristics and a beta-pleated shape. The deposition of these proteins in the heart and the involvement of the autonomic nervous system make it challenging to manage heart failure (HF) in these patients. Given this scenario, This article aims to demonstrate how to manage HF in patients with cardiac amyloidosis.
Keywords: Amyloidosis; Heart Failure; Therapeutics
1,333