ABC Heart Fail Cardiomyop 2021; 1(1): 33-43
Possible Mechanisms of Action of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure
Abstract
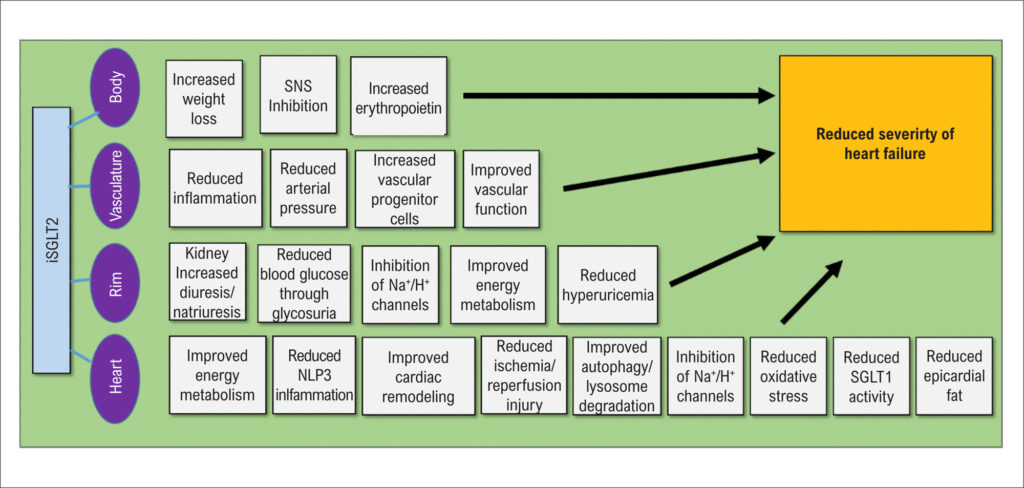
In mid-2013, sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors such as canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin were introduced as possible treatments for type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2). Cardiovascular safety studies demonstrated that not only were SGLT2 inhibitors safe, but they were also associated with a significant reduction in cardiovascular mortality and heart failure (HF) outcomes including hospitalizations. These findings encouraged the development of clinical trials aimed specifically at investigating the effects of this new drug class on HF with reduced ejection fraction (EF), including the DAPA-HF and EMPEROR-reduced studies. The demonstration of beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on the reduction of cardiovascular events in treated patients with symptomatic HF and reduced left ventricular EF (LVEF < 40 %) resulted in the extension of SGLT2 inhibitor indication to patients with symptomatic HF with reduced EF. The mechanisms behind these beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors are not entirely known. In this review, we analyze several current hypotheses for the cardioprotective effects of SGLT2 inhibitors, including reduced blood pressure, increased natriuresis, improved energy metabolism, prevention of inflammation, weight loss, improved glycemic control, inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system, prevention of myocardial remodeling, prevention of ischemia/reperfusion injury, inhibition of Na+/H+ channels, increased autophagy and lysosomal degradation, SGLT1 inhibition, reduced hyperuricemia, reduced epicardial fat, increased erythropoietin levels, increased progenitor/precursor cells, reduced oxidative stress, and improved vascular function.
3,288