ABC Heart Fail Cardiomyop 2025; 5(1): e20240062
Cardiac Sarcoidosis and Complex Arrhythmias
Introduction
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory granulomatous disease of unknown cause, related to genetic factors, with an incidence of 1 to 30 cases/100,000 people, and is more prevalent in women over 50 years of age. The formation of scar tissue characterizes it and can affect any organ, with a predilection for the lungs in approximately 90% of cases. Patients with cardiac involvement are mainly male and, in general, have a worse prognosis, with high mortality rates observed in this population (85% of deaths).,
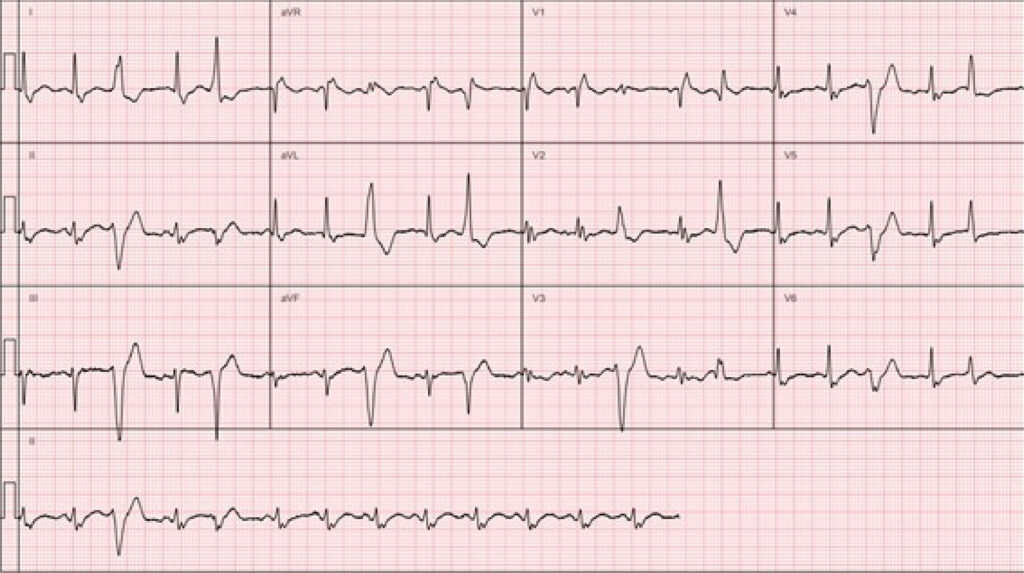
The scar substrate in the myocardium, which presents as multifocal and heterogeneous, is related to several cardiac manifestations. Among the most common, we can mention left ventricular dysfunctions, atrioventricular conduction abnormalities, and ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation, which can lead, in some cases, to sudden death. In view of this, the use of antiarrhythmic drugs is necessary in clinical practice in most patients, aiming at the control of arrhythmias, especially those of ventricular origin, and consequently improving the quality of life and reducing mortality. In this work, we report the therapeutic management of a case of cardiac sarcoidosis associated with prolonged QT interval that evolved with complex ventricular tachycardia (VT).
[…]
Keywords: Cardiac Arrhythmias; Long QT Syndrome; Sarcoidosis
307