ABC Heart Fail Cardiomyop 2024; 4(4): e20240060
Heart Failure Treatment with SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background
Heart failure (HF) is a clinical diagnosis of a condition that develops secondary to either left ventricular systolic or diastolic functions. Lately, inhibitors of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) have been added to the list of drugs used in the management of HF.
Objectives
To compare the efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors to traditional treatment in hospitalization and death for HF.
Methods
Relevant databases were searched for articles published until October 2023. Out of 24 nonduplicated screened studies, 11 studies were selected. The primary analysis was for cardiovascular death, and the secondary analysis was for hospitalization for HF.
Results
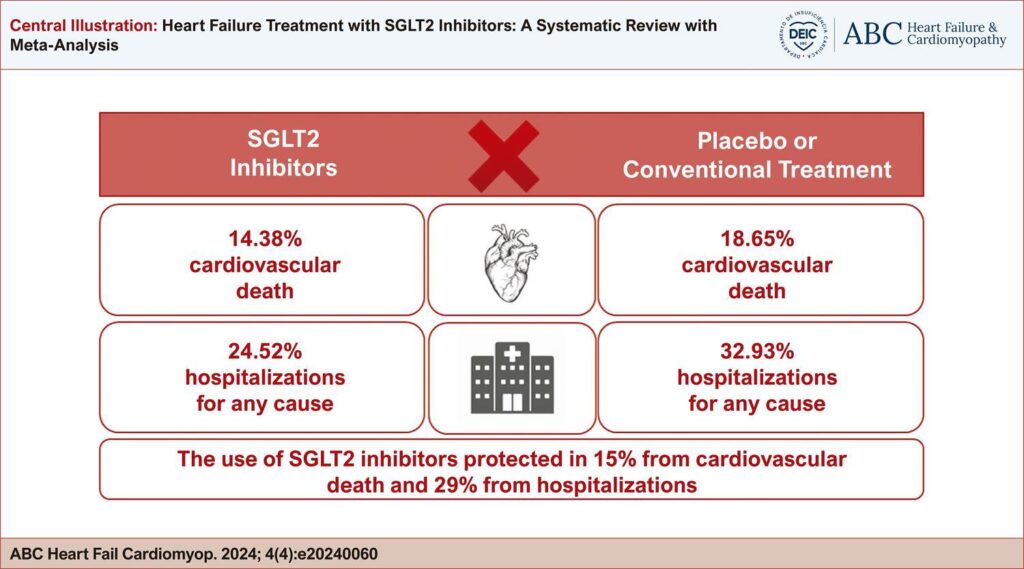
We selected 11 for the systematic review and 8 studies for quantitative analysis, accounting for 54,381 patients from over 800 health centers worldwide. The use of SGLT2 inhibitors significantly reduced cardiovascular death in all patients when compared to placebo (HR 0.85, 95%CI 0.78-0.91) and also reduced hospitalizations for HF (HR 0.71, 95%CI 0.67-0.76).
Conclusions
Patients with HF in the use of SGLT2 inhibitors have a better outcome than those with conventional treatment; SGLT2 inhibitors protect 15% from cardiovascular death and 29% from hospitalizations.
731